Rethinking Copyright in the Age of Generative AI
Striking a balance between incentives and innovation
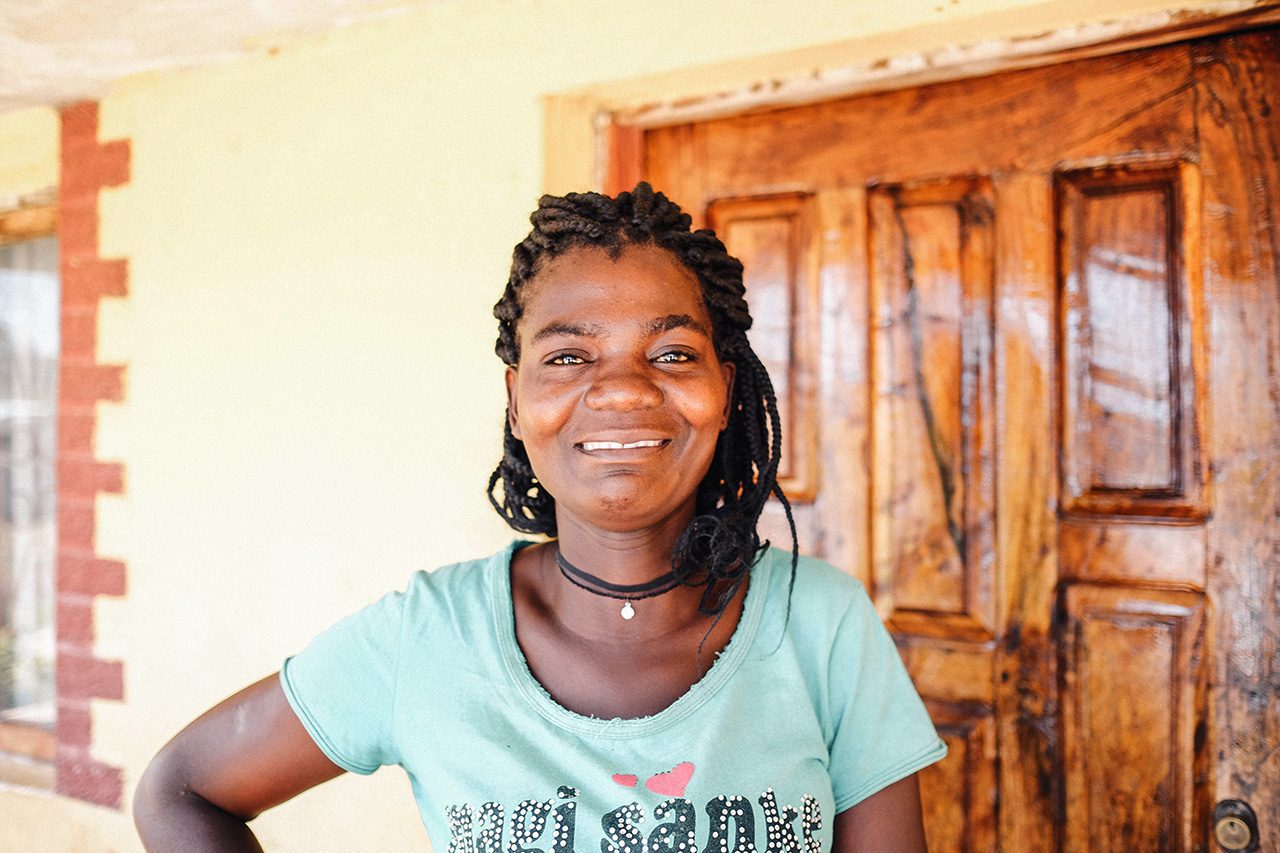

Berta Jambo, Mozambican farmer and community leader
“One entrepreneur can change their community and millions can change the world”
Across the globe, women-led businesses pose a “risk” for most financial institutions – securing smaller bank loans with higher interest rates. In developing economies, they make up 23% of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and own 32% of the overall financing gap. The Women’s World Banking shows nearly one billion women unserved or underserved by the formal finance sector.
“Lack of access to capital limits their (women’s) ability to grow their businesses, invest in their communities, and reach their full economic potential,” says Lizz Welch, CEO of the Denver-based International Development Enterprises (iDE), which bridges the gender financing gap by investing $137 million in the last five years across Asia, Africa, and Central America “powering entrepreneurs to end poverty” in agriculture, water, and sanitation sectors.

International Development Enterprises CEO, Lizz Welch (photo credit: iDE)
In developing countries, says Welch, stringent collateral requirements and higher interest rates also pose gender bias. Since most women don’t own assets, banks prefer a husband’s name on a loan without direct “investment in the woman’s business”.
iDE’s 1,300 global staff design financially competitive market ecosystems that remain climate resilient and inclusive of marginalized people. Investments in women-led social enterprises in the agriculture and sanitation sectors also support many toilet business owners selling safe and hygienic toilets to Asian and African rural households – including iDE-owned, woman-led Cambodian water filter company, Hydrologic, providing affordable water filters to rural households.
iDE’s unique international development process increases the livelihoods of fund recipients by “powering entrepreneurs to thrive on their own terms.” Sustainably increased incomes and health of clients, their families, and communities, create economic empowerment, enabling investment in education, starting/expanding a business, and medical care for family members.
“We use market-based approaches that align the incentives of our clients (sustainable business income) with their customers (affordable products and services that increase their own incomes sustainably). Because relationships between our clients and customers are built on trust, respect, and delivering results for the customer, the relationships are sustainable — both parties have aligned incentives to continue working and expanding their partnership,” explains Welch.
iDE’s 1,300 global staff design financially competitive market ecosystems that remain climate resilient and inclusive of marginalized people.
Working with community-based savings and lending groups empowering women’s access to capital – iDE tilts the funding scale for women who pay off their loans. iDE introduces them to rural banks and supports their bank loan application process.
“We also work directly with banks to design and develop appropriate loan instruments that specifically meet the needs of women entrepreneurs for their sector – agriculture, sanitation, etc.– to lower collateral requirements that prevent women from accessing capital in the first place,” Welch says.
Over the last five years, iDE has deployed 53% of its funding in Asia – 43% and 4% across Africa and Central America respectively. As growth and development sectors shift so do iDE’s funding trends – investing 51% in Africa in 2022, and 45% and 3% respectively in Asia and Central America.

Bangladesh – the world’s 8th most densely populated country of 170 million population – hosts iDE’s most impactful and oldest (since 1983) programs – accounting for 55% of the impact on individuals. It’s due to cost-effective scaling without additional time and cost as required in sparsely populated countries.
“As our funding levels rise in each country, so does our impact. Currently, we see a higher funding trend from government-level donors toward Africa,” Welch says iDE’s largest program is in Mozambique, overtaking Bangladesh and Cambodia.
Focusing on annual household income increases, iDE’s performance metrics in the agriculture sector marked the highest annual income increases in Cambodia ($1,459), Nepal ($690), Zambia ($518), Ethiopia ($469), and Mozambique with $456. Across the water, sanitation, and hygiene-funded sectors, Bangladesh had the highest livelihood savings of $246 followed by $110 in Cambodia.
Overall, iDE investments have impacted:
According to UN Women, climate change gender impact is a “threat multiplier” escalating social, political, and economic tensions in fragile and conflict-affected settings. Driving conflicts exacerbate women and girls’ vulnerability to all forms of gender-based/conflict-related violence.
“Focusing on the evidence-based impact of prioritizing women as catalysts of sustainable change, iDE invests in women believing that it is not just the right thing to do but also the smart thing to do,” says Welch. “Across developing economies, women are more impacted by the effects of climate change, while also well positioned (in the household and community) to contribute to strategies that address changing environmental realities.”

Women agricultural entrepreneurs’ knowledge base addresses climate challenges ranging from planting drought-resistant seeds to producing fortified crops to combat malnutrition. Women produce nearly 80% of the food in low and middle-income economies, and secure household drinking water and energy.
Among many success stories is iDE-trained Farm Business Advisor, Berta Jambo, a Mozambican farmer and community leader who secured a guaranteed cabbage delivery contract with local hospitals. Her reliance on trust-based partnerships with hospitals – and an agro-dealer who provides her seeds, fertilizers, and micro-irrigation equipment – allow Berta to provide regular cabbage deliveries to hospitals. And profits are distributed among community farmers.
Berta’s “trust-based” relations were a lifeline in 2019 when Category 4 tropical cyclone Idai killed over 1,500 and destroyed thousands of farms. Her agro dealer offered seeds on consignment, which Berta distributed in her community of farmers. Within one month, the collective reached pre-Cyclone production levels. Regular hospital cabbage deliveries resumed, and the women rebuilt their lives profitably.
“Globally, on average, female entrepreneurs and women-led businesses deliver higher financial returns than male-led businesses. In particular, women-led SMSEs are recognized by the International Finance Corporation as better at both investing in their families’ health and education, as well as reinvesting profits back into their businesses. This dual focus has a profound impact on strengthening the local economy and the communities where the women leading these SMEs live,” Welch says.
Women entrepreneurs deliver greater business results and inclusive growth returns, for a number of reasons, explains Welch.
iDE’s customers’ and suppliers’ training includes financial literacy, improved, climate-resilient farming practices, and product marketing strategies. “
One of the main challenges our clients face is lack of connection to suppliers — shops/retailers/input suppliers typically don’t see value in servicing last-mile customers who are hard to reach, have low incomes, and live in sparsely populated locations. Part of iDE’s work involves training farmers on climate-resilient and improved farming practices and then supporting aggregation efforts to bring multiple farmers together to sell their crops with greater bargaining power,” Welch says. Aggregated crops offer financial viability of remote, low-income farmers to suppliers by achieving scale and reduced logistical costs like transportation.
Farmers purchasing and effectively “using inputs and tools because they are earning higher incomes” help create “a virtuous cycle and stronger relationships.”
Evidence shows women entrepreneurs as “impact-multipliers in their families and their communities” provide up to 70% of agricultural labor in developing countries. This constitutes a significant share of iDE’s potential entrepreneurial clients.
Empirical studies, Welch says, confirm that if women farmers were “given the same agricultural inputs, tools, and financial resources as men, their agricultural yields would increase by 20 to 30%; national agricultural production could rise by up to 4%; and the global number of undernourished people could drop by 100–150 million people.”
“We know that the way we support women entrepreneurs in the agricultural sector must be contextualized to engage with the specific barriers they face,” Welch says. In comparison to men entrepreneurs, women make higher investments and reinvest their earnings in long-term health and education, children’s well-being, other women, and in communities – and employ six times more female employees than male-led SMSEs.
Related Content
Comments
Deep Dives
RECENT
Editor's Picks
Webinars

Featuring
Lizz Welch & Jennifer Roglà
iDE
May 16 - 12:00 PM EST

Impact Encounters
May 22 - 6:30 PM EST
News & Events
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive updates about new Magazine content and upcoming webinars, deep dives, and events.
Become a Premium Member to access the full library of webinars and deep dives, exclusive membership portal, member directory, message board, and curated live chats.
0 Comments